The plant structure describes the hierarchical organization of a technical plant into logical and functional units. The plant structure can vary depending on the application, but typically it consists of three levels: Plant, Hardware Zone and Sequence. The Plant level is the top level of the plant structure and represents the entire plant. The Plant level is used to clearly represent and organize the plant and to assign global parameters and functions. The hardware zone level is the middle level of the plant structure and divides the plant level into smaller sections, each containing a specific hardware component or module. The hardware zone level is used to define and configure hardware interfaces and properties and to manage resources and security aspects. Each hardware zone has independent automatic and manual controls. The Sequence level is the lowest level of the system structure and describes the sequences and processes within a hardware zone. The sequence level is used for programming and controlling the logical functions and algorithms as well as for monitoring and diagnosing the operating status. The sequence level is divided into different layers.
Structure of the Selmo project
The system structure is always the same:
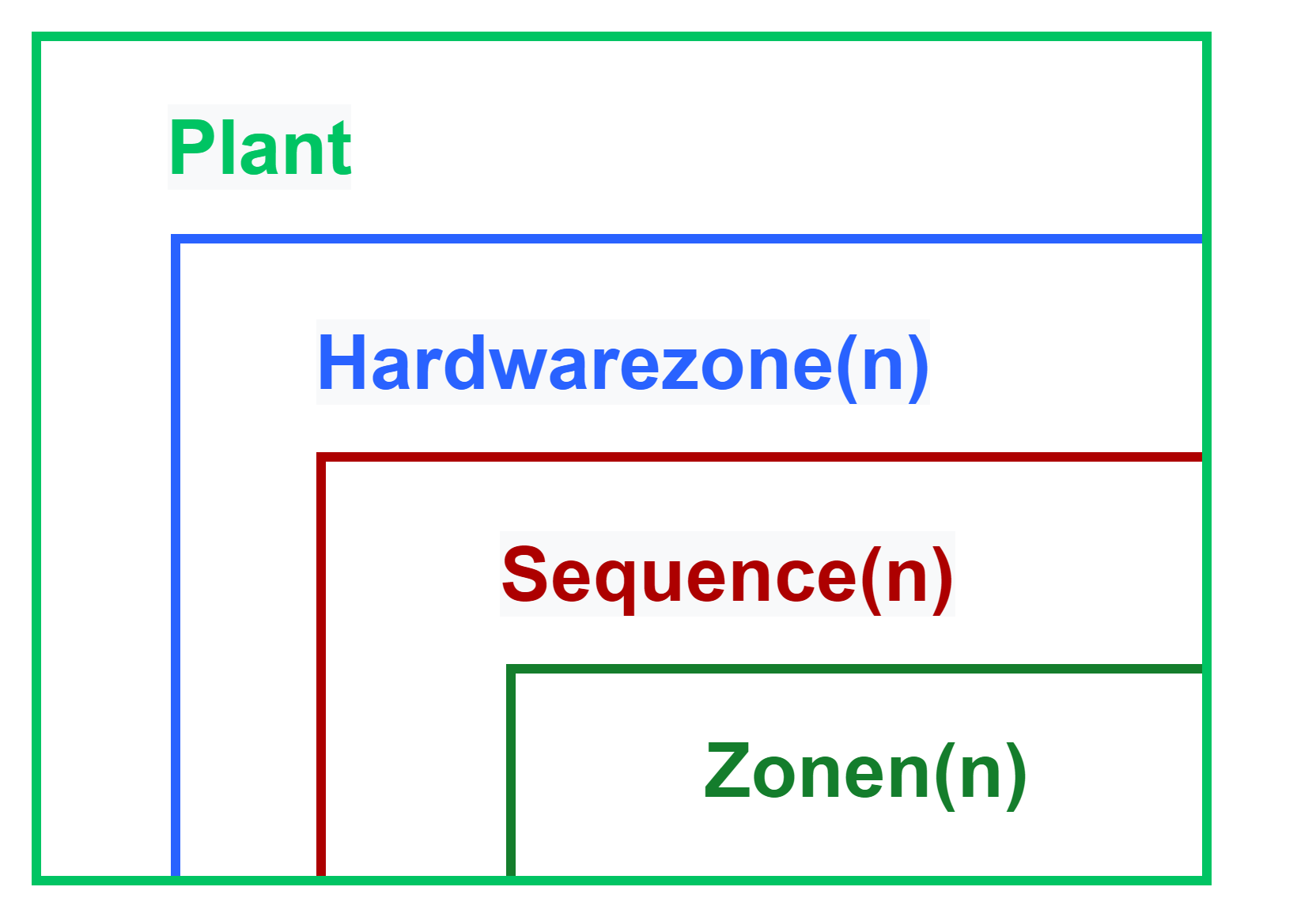
This consists of different layers. The top level is called the Plant and represents the overall system. The Plant always contains at least one sublevel, the hardware zone(s). The hardware zone can contain one or more Sequences. A Sequence is always assigned to only one hardware zone. A Sequence is a subsystem that defines a logical process description. This consists of a logical process description in the form of a step chain (Logic Layer), the definition of states by zones (System Layer), the interlocks in manual mode (MXIC) and constantly monitored zones (CMZ).
Plant
In industry, the term "Plant" usually refers to a facility or equipment used to manufacture or process products or raw materials. For example, this may be a factory, plant, power station, or refinery. A Plant often includes multiple units that operate in a specific sequence to produce the desired product or process the raw material. These may include manufacturing equipment, machinery, chemical reactors, storage and supply facilities, or control systems. Plants can be very large and complex often requiring specialized knowledge and skills to operate and maintain. Therefore, multiple professionals such as engineers, technicians, and laborers typically work together to operate a Plant and achieve optimal performance.
Hardware Zone (HWZ)
A hardware zone (HWZ for short) is a specific area of a machine or cell area with separate automatic and manual controls. Each hardware zone has its own specific overview. The size of a hardware zone depends on the configuration of the machine or cell and can contain and control one or more step sequences.
Sequence
A sequence control is a type of control system that executes a sequence of predefined steps or states. An example of a sequence controller is a step controller, which consists of a series of memory elements, each representing a step in the sequence. A step controller can be controlled by external input signals or internal logic. A sequence controller can be used to automate or synchronize complex processes, such as manufacturing in a factory or communications in a network.
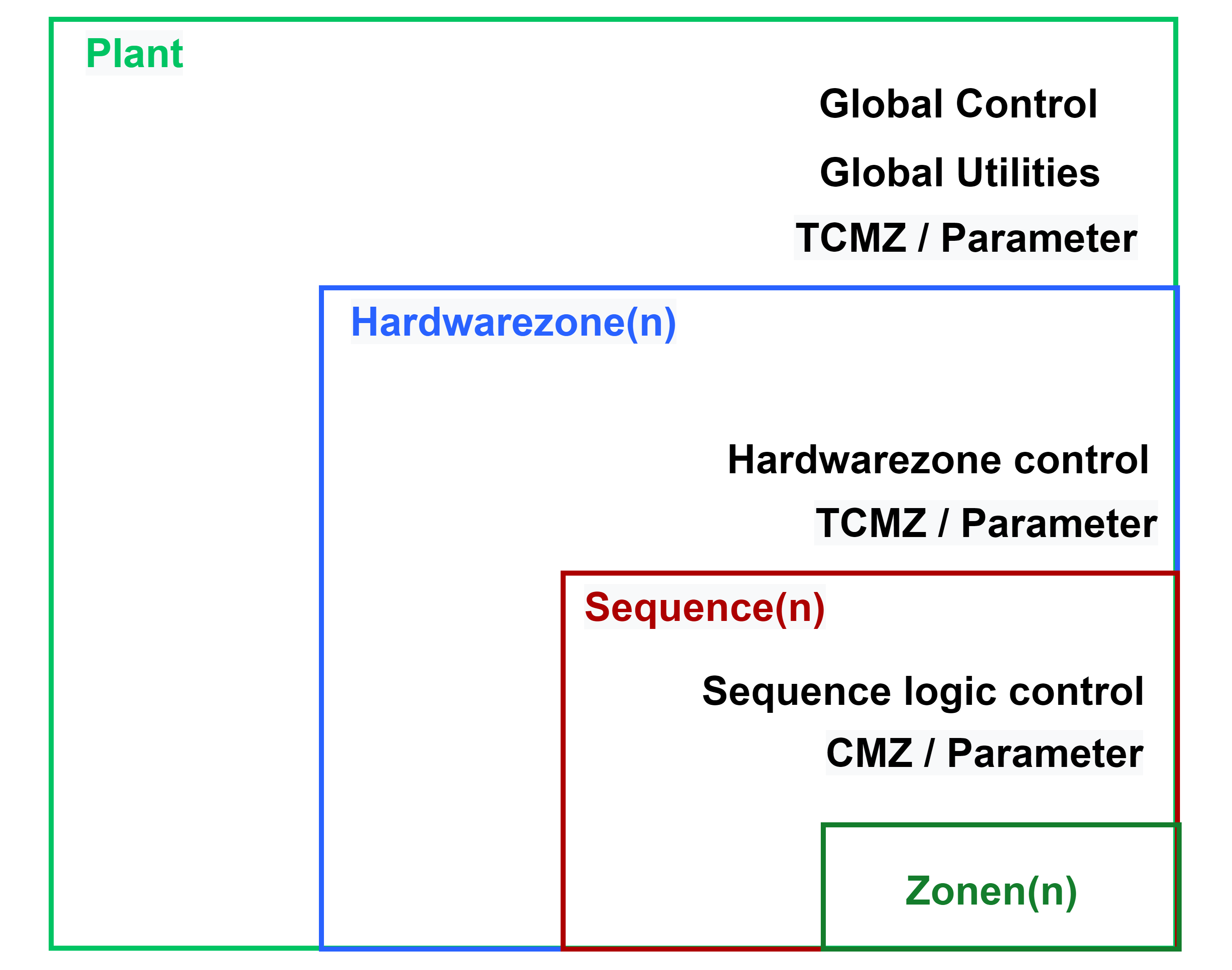
Elements of Plant, Hardware Zone and Sequence
Each level of a Selmo project has certain properties and functions that apply in the effective area. The elements and its effective area are described in the following figure: